Proxy Application Destinations
*All screenshots are from the UltraPort HL7 Postmaster
 .
.
With a 'Proxy' destination you enter the TCP/IP address (if the Proxy Application is running on a remote computer) and enter the "Interface Port Number" which the Proxy application will use to receive HL7 messages sent to it by the Postmaster. Proxy applications are created using the UltraPort Postmaster API toolkit for Microsoft Visual Studio (see Proxy Application Development for more information). For this to work you must either have the application installed and running on this computer or on a computer connected to this computer (within the same LAN, WAN or VPN).
In addition to creating your Proxy Application Destination in the Postmaster you must also insure that the Proxy application itself is configured to receive HL7 messages sent by the Postmaster on the Interface Port Number you enter in the Postmaster Proxy destination properties.
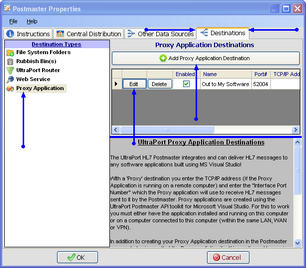
To Create a New Proxy Application Destination
First. Edit the selected postmaster (see Creating and Editing Postmasters) and select the Other Data Sources tab. In the Other Data Sources tab select File System Folders in the Destination Types list.
Second. If creating a new folder data source click the ![]() Add Proxy Application Destination button, otherwise click the 'Edit' button next to one of the existing destinations in the list to open up the Proxy Destination properties window. In the properties window fill out steps 1 through 5 and click
Add Proxy Application Destination button, otherwise click the 'Edit' button next to one of the existing destinations in the list to open up the Proxy Destination properties window. In the properties window fill out steps 1 through 5 and click ![]() to save your destination.
to save your destination.
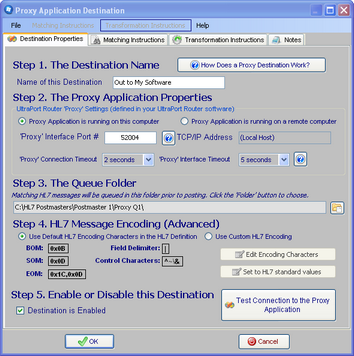
Step 1. The Destination Name. All Postmaster objects (data sources and destinations) must have a unique name. It's completely user defined and alpha-numeric and follows the same rules as creating a file or folder name in MS Windows.
Step 2. The Proxy Application Properties. The values you enter in Step 2 are largely determined by the other application. Since the HL7 Postmaster is going to be "Sending" HL7 messages to the Proxy Application they have to tell YOU which Port Number they are using to receive HL7 from the postmaster and (if they are running on a remote computer) what the TCP/IP Address is for that computer. In addition you need to set the Proxy Connection Timeout and the Proxy Interface Timeout.
Extended Feature: Test the connection to the Proxy Application. If you've entered all of the values in Step 2 you can test the connection to the Proxy Application (it must be running and waiting for HL7 messages) by clicking this button:
![]()
Step 3. The Queue Folder. Even if the Proxy Application at the other end of your destination is not running, the Postmaster will continue to deliver HL7 messages to it by "Queuing" up the messages in the Queue folder until the Proxy Application comes back online. Click the ![]() button to browse for the folder which the postmaster should use for this.
button to browse for the folder which the postmaster should use for this.
Step 4. HL7 Message Encoding (Advanced). The HL7 Encoding characters instruct HL7 parsers in how to properly "read" an HL7 message. Changing this from the default is RARELY needed. A good general rule of thumb is this test: If you don't KNOW whether or not you need to change the HL7 Message Encoding then you don't need to change it, and you should just leave it as the default.
Step 5. Enable or Disable this Destination. Check the box to enable the destination, uncheck it to disable the destination.
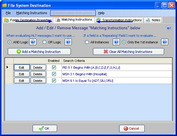
Extended Feature (Optional): You can enter Matching Instructions to filter the HL7 messages delivered to the proxy application:
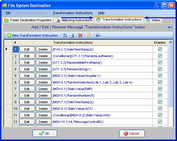
Extended Feature (Optional): You can enter Transformation Instructions to dynamically change HL7 message data BEFORE it is delivered to the destination:
Extended Feature (Optional): You can also enter your own "Notes" about Postmaster Objects (data sources and destinations) using the 'Notes' tab.
For information about how to configure a Proxy application to receive HL7 messages sent by the UltraPort HL7 Postmaster you will have to refer to the documentation for that application.
See Also: Proxy Application Development, Matching Instructions, Transformation Instructions